What is QSFP56 – It is an optical fiber connector format that uses a single-mode fiber for transmission. It has a maximum distance of 300 meters and can carry up to 500Mbps per lane. QSFP 56 is commonly used to connect high-speed devices in the data center.
Table of Contents
What does it Do?
QSFP is a marketing term used to describe the connection technology of QLogic’s family of high-speed Gigabit Ethernet adapters. With QSFP56, you can attach devices such as network interface cards (NICs) and transceivers to your QLogic switches with only one cable. This reduces clutter and makes cabling easier.
How to Use It?
QSFP is a short form for Quasi-Synchronous Fibre Channel Protocol. A QSFP module connects two devices in the same LAN that share a common fibre channel fabric, such as switches, routers and storage area networks (SANs). It uses existing Ethernet cabling to connect the devices.
The QSFP module is inserted into a port on one of the devices. The other device searches for and connects to the QSFP module. The QSFP module provides an interface between the Ethernet network and Fibre Channel fabric.
You can use QSFP modules in servers, switches and routers. You can also connect them to SANs.
What are the Benefits of QSFP56?
QSFP is short for QuickSwitch Fiber Channel and it is a fiber optic connectivity technology that was initially designed for use in high-performance switches. QSFP enables the connection of multiple Fibre Channel devices over a single physical port. This makes QSFP ideal for connecting servers, storage arrays, and other Fibre Channel nodes within a data center.
There are several benefits to using QSFP with your data center infrastructure. First, QSFP provides increased bandwidth and performance compared to traditional fiber optic connections. This is due to the fact that each device connected via QSFP can share bandwidth more effectively than devices connected via traditional copper cables. Second, QSFP provides greater reliability than traditional Fibre Channel connections. This is because there is no cabling involved in the connection, which eliminates potential points of failure. Finally, QSFP supports advanced security features such as Data Encryption Standard (DES) and Triple DES (3DES), which increases the protection of your data against unauthorized access.
Necessary Precautions when using QSFP56
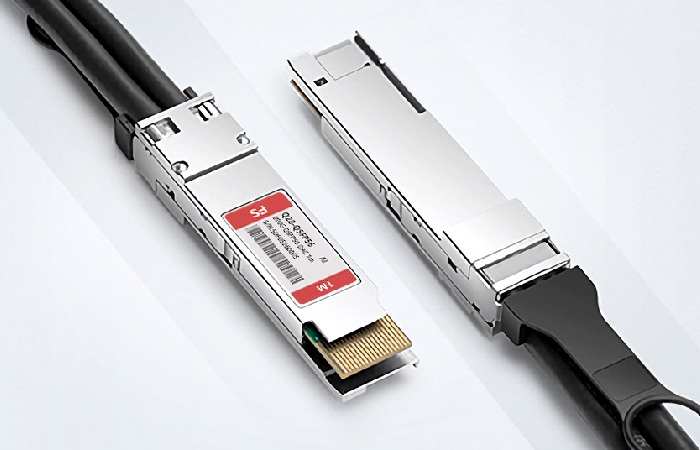

QSFP is a type of fiber optic cable designed for short-reach applications such as data center interconnects and backbones. It uses 50-micron diameter fibers that are bundled into a single cable, which provides higher bandwidth and lower latency than traditional fiber optic cables.
To prevent damage to the fiber, it’s important to follow some basic precautions when using QSFP:
- Always use the correct connector. The connector should be compatible with the cable and the equipment it’s being used with. Make sure to read the manufacturer’s instructions before connecting the cable.
- Keep the cable clean. Dirt or other objects can damage the fibers inside the cable, causing delays or even loss of data transmission. Cleaning procedures vary depending on the type of QSFP, but generally you’ll need to use some sort of cleaning solution and brush or swab to remove dirt and dust build-up.
- Avoid kinking or bending the cable excessively. These actions can cause stress on the fibers inside the cable, which can lead to premature failure.
Things to know about QSFP56
QSFP is a short form for Quick-Start Fiber Optic PCI Express. It is a single-mode, multimode fiber optic cable designed to connect servers and switches in a network. QSFP provides high bandwidth and low latency for fast networking between servers and switches.
And also, QSFP supports the following wavelengths: 850nm, 1310nm, 1550nm, and 1750nm. QSFP can be used with both active and passive cabling solutions. It has a small form factor that allows it to be installed in tight spaces.
What are the Side Effects of using QSFP56?
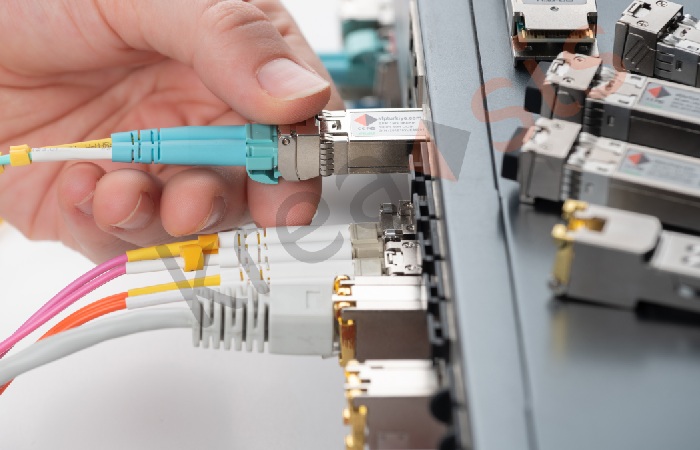

QSFP is an optical networking interface standard that can provide up to 1.3 Gbps per link. It uses a short wavelength communication, which makes it ideal for connecting devices in the 10-GbE and 40-GbE classes of Ethernet. QSFP also supports data rates up to 10 Gb/s over cable, making it ideal for high-speed applications such as video streaming, data center interconnect, and machine-to-machine (M2M) communications.
Like many other optical networking interfaces, QSFP has both benefits and drawbacks. The primary benefit of using QSFP is that it can provide high-speed connectivity over long distances. However, like most other optical networking interfaces, QSFP suffers from a limited number of ports and requires a special connector known as a QSFP+ breakout box. Additionally, because QSFP uses short-wavelength light, it can experience significant performance degradation when passing through walls or other obstacles.
For more info check this site: www.technologywebdesign.com
